The Future of Web Dev
The Future of Web Dev
JSON-Native UI Components for AI Conversations – Tool UI
React component framework for AI chat interfaces. Converts JSON responses into inline components. Built on Radix, Tailwind, and shadcn/ui.
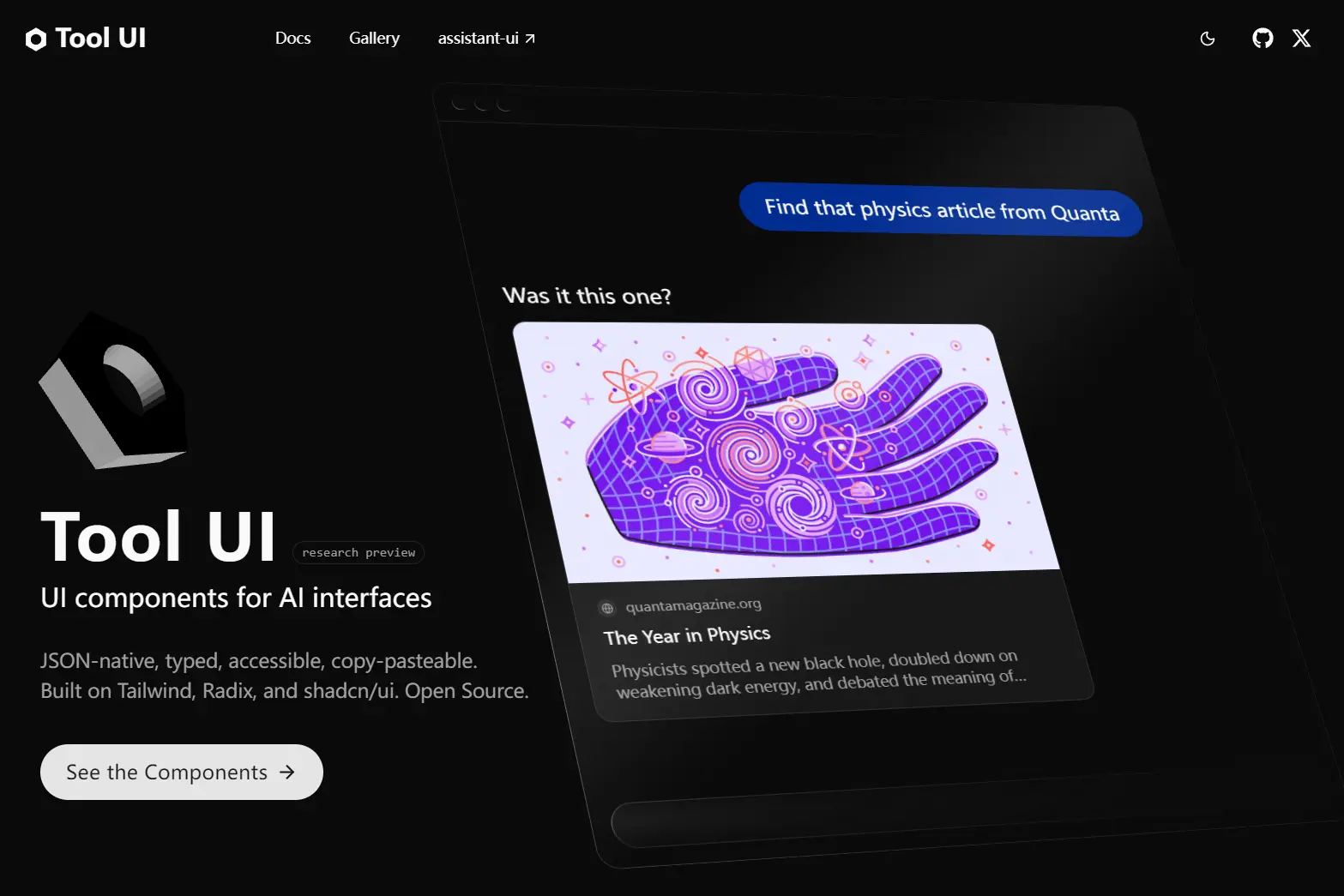
Tool UI is a React component framework that transforms JSON outputs from AI models into interactive, conversation-native user interfaces.
It functions as a rendering layer that sits on top of primitives like Radix UI and shadcn/ui while connecting to orchestration tools such as the Vercel AI SDK or LangGraph.
This framework handles the full lifecycle of an AI interaction, from the initial tool call to the final user receipt. It serializes component data on the server and parses it on the client to maintain type safety across the network boundary.
You can define tools using Zod schemas, and the Tool UI maps these definitions to specific React components like charts, approval cards, or code blocks.
Features
🎯 Conversation-native components: Components render inside message threads at chat width.
🔧 Schema-first architecture: Every component accepts serializable JSON with stable IDs.
🤖 Assistant-anchored rendering: The assistant introduces each surface, provides context, and generates follow-up responses based on user interactions.
⚡ Stack-agnostic integration: You can connect it to any LLM provider.
✅ Type safety: Server schemas validate outputs before sending.
📱 Mobile-optimized layouts: All components scale down to narrow viewports.
♿ Accessibility: Components inherit ARIA patterns from Radix primitives.
🔄 Lifecycle management: Each component tracks its state from invocation through completion.
🎨 Themeable surfaces: Components respect your Tailwind config.
📊 Interactive controls: Your app processes confirmations via callbacks or server actions.
🔍 Reference support: Stable IDs let the assistant mention specific elements.
📦 Production components: The library includes charts, data tables, image galleries, code blocks, video players, terminal output, and more.
How to Use It
Installation
Run the assistant-ui CLI to bootstrap your project. The CLI configures assistant-ui runtime, installs dependencies, and sets up your file structure.
npx assistant-ui@latest initIf you want manual control, install packages directly.
pnpm add @assistant-ui/react @assistant-ui/react-ai-sdk ai @ai-sdk/openai zodAdd your OpenAI API key to your environment.
OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-...Basic Setup with AI SDK
Create a runtime provider that connects your frontend to your chat API.
"use client";
import { AssistantRuntimeProvider } from "@assistant-ui/react";
import {
useChatRuntime,
AssistantChatTransport,
} from "@assistant-ui/react-ai-sdk";
function App() {
const runtime = useChatRuntime({
transport: new AssistantChatTransport({ api: "/api/chat" }),
});
return (
<AssistantRuntimeProvider runtime={runtime}>
{/* Your chat UI components */}
</AssistantRuntimeProvider>
);
}The AssistantChatTransport handles message streaming and tool execution between your frontend and the AI SDK endpoint.
Server-Side Tool Definition
Define a backend tool that returns schema-validated JSON matching a Tool UI component.
import { streamText, tool, convertToModelMessages, jsonSchema } from "ai";
import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
import { SerializableLinkPreviewSchema } from "@/components/tool-ui/link-preview/schema";
export async function POST(req: Request) {
const { messages } = await req.json();
const result = streamText({
model: openai("gpt-4o"),
messages: await convertToModelMessages(messages),
tools: {
previewLink: tool({
description: "Show a preview card for a URL",
inputSchema: jsonSchema<{ url: string }>({
type: "object",
properties: { url: { type: "string", format: "uri" } },
required: ["url"],
additionalProperties: false,
}),
async execute({ url }) {
return {
id: "link-preview-1",
href: url,
title: "Example Site",
description: "A description of the linked content",
image: "https://example.com/image.jpg",
};
},
}),
},
});
return result.toUIMessageStreamResponse();
}The SerializableLinkPreviewSchema enforces the exact shape of your component props. The schema includes required fields like id, href, and title. Your execute function fetches real data and returns it in the schema format.
Client-Side Component Registration
Connect your backend tool to a frontend component.
import { makeAssistantToolUI } from "@assistant-ui/react";
import {
LinkPreview,
LinkPreviewErrorBoundary,
parseSerializableLinkPreview,
} from "@/components/tool-ui/link-preview";
export const PreviewLinkUI = makeAssistantToolUI({
toolName: "previewLink",
render: ({ result }) => {
if (result === undefined) {
return (
<div className="bg-card/60 text-muted-foreground w-full max-w-md rounded-2xl border px-5 py-4 text-sm shadow-xs">
Loading preview…
</div>
);
}
const preview = parseSerializableLinkPreview(result);
return (
<LinkPreviewErrorBoundary>
<LinkPreview {...preview} maxWidth="420px" />
</LinkPreviewErrorBoundary>
);
},
});The toolName must match your backend tool name exactly. The parser validates the result at runtime and returns typed props. Mount <PreviewLinkUI /> inside your AssistantRuntimeProvider to register it.
function App() {
return (
<AssistantRuntimeProvider runtime={runtime}>
<PreviewLinkUI />
<Thread />
</AssistantRuntimeProvider>
);
}When the LLM calls previewLink, assistant-ui automatically renders your component with the returned data.
Frontend Tools with User Interactions
Some components handle user decisions rather than just displaying information. Option List components let users choose from presented options. You register these as frontend tools.
First, configure your backend to forward frontend tool definitions.
import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
import {
streamText,
convertToModelMessages,
jsonSchema,
type UIMessage,
type JSONSchema7,
} from "ai";
type ForwardedTools = Record<
string,
{ description?: string; parameters: JSONSchema7 }
>;
function toStreamTextTools(tools?: ForwardedTools) {
if (!tools) return undefined;
return Object.fromEntries(
Object.entries(tools).map(([name, tool]) => [
name,
{
...(tool.description ? { description: tool.description } : {}),
inputSchema: jsonSchema(tool.parameters),
},
]),
);
}
export async function POST(req: Request) {
const body = (await req.json()) as {
messages: UIMessage[];
system?: string;
tools?: ForwardedTools;
};
const result = streamText({
model: openai("gpt-4o"),
messages: await convertToModelMessages(body.messages),
system: body.system,
tools: toStreamTextTools(body.tools),
});
return result.toUIMessageStreamResponse();
}The AssistantChatTransport sends registered frontend tools in the request body. Your endpoint forwards them to the LLM so it knows which tools it can call.
Create the frontend tool with user interaction handling.
"use client";
import { makeAssistantTool } from "@assistant-ui/react";
import {
OptionList,
parseSerializableOptionList,
SerializableOptionListSchema,
type SerializableOptionList,
type OptionListSelection,
} from "@/components/tool-ui/option-list";
export const SelectFormatTool = makeAssistantTool<
SerializableOptionList,
OptionListSelection
>({
toolName: "selectFormat",
description: "Ask the user to choose an output format.",
parameters: SerializableOptionListSchema,
render: ({ args, result, addResult, toolCallId }) => {
if (!Array.isArray((args as any)?.options)) return null;
const optionList = parseSerializableOptionList({
...args,
id: (args as any)?.id ?? `format-selection-${toolCallId}`,
});
if (result !== undefined) {
return (
<OptionList {...optionList} value={undefined} choice={result} />
);
}
return (
<OptionList
{...optionList}
value={undefined}
onConfirm={(selection) => addResult(selection)}
/>
);
},
});The component waits for required fields to arrive before rendering. The addResult callback sends the user selection back to the conversation. The component displays a receipt state after confirmation.
Mount the tool component to register it.
<AssistantRuntimeProvider runtime={runtime}>
<SelectFormatTool />
<Thread />
</AssistantRuntimeProvider>Auto-Continue After User Input
Configure the runtime to automatically continue the conversation after the user confirms a decision.
import {
useChatRuntime,
AssistantChatTransport,
} from "@assistant-ui/react-ai-sdk";
import { lastAssistantMessageIsCompleteWithToolCalls } from "ai";
const runtime = useChatRuntime({
transport: new AssistantChatTransport({ api: "/api/chat" }),
sendAutomaticallyWhen: lastAssistantMessageIsCompleteWithToolCalls,
});The assistant processes the user choice immediately instead of waiting for the next message.
Using Components Without assistant-ui
Copy components directly into your project if you want manual control. Tool UI components work with any React app. You parse tool outputs yourself and pass props to components.
import {
LinkPreview,
parseSerializableLinkPreview,
} from "@/components/tool-ui/link-preview";
function MyChat() {
const toolOutput = {
id: "preview-1",
href: "https://example.com",
title: "Example",
description: "A site description",
};
const preview = parseSerializableLinkPreview(toolOutput);
return <LinkPreview {...preview} maxWidth="420px" />;
}Always include the shared directory when copying components manually. It contains action buttons, schemas, and formatters that all components depend on.
Available Components
Information surfaces display read-only content. Link Preview shows website metadata. Image and Image Gallery render media with attribution. Video and Audio handle playback. Code Block displays syntax-highlighted code. Chart visualizes data with interactive controls.
Decision surfaces handle user choices. Approval Card presents binary confirmations for agent actions. Option List supports single or multi-select with response actions. Parameter Slider adjusts numeric values.
State surfaces show progress or results. Order Summary displays itemized purchase details with pricing. Plan shows step-by-step task workflows. Terminal renders command-line output.
Composite surfaces combine multiple elements. Data Table includes sortable columns and row actions. Item Carousel creates horizontal browsing layouts. Social Post renders platform-specific formats for Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn.
Related Resources
- Radix UI: Unstyled, accessible component primitives.
- shadcn/ui: Copy-paste component library using Radix and Tailwind.
- AI SDK: Vercel’s framework for LLM integration.
- assistant-ui: React runtime for AI chat interfaces.
FAQs
Q: Can I use Tool UI without assistant-ui?
A: You can copy components directly and handle tool parsing manually. The components work with any React setup. Assistant-ui provides the runtime that automatically connects tool calls to component rendering. Without it, you parse JSON outputs yourself and pass props to components.
Q: How do I add custom styling to components?
A: Components use Tailwind utility classes and respect your theme configuration. Override default colors and spacing through CSS variables in your tailwind.config. Each component accepts a className prop for additional styles. You can also fork components and modify their internal markup.
Q: Does Tool UI support streaming tool outputs?
A: Tool outputs stream from the LLM to your frontend. Components handle partial data gracefully. Required fields may arrive incrementally. The render function checks for field availability before displaying content. Loading states show until complete data arrives.
Q: What happens if a tool output fails schema validation?
A: Parser functions throw errors when validation fails. Error boundaries catch these exceptions and display fallback UI. Check your tool outputs match component schemas during development. The type system catches most mismatches before runtime.